Workflow Statistics
Chaos injections often tends to disrupt tightly coupled micro-services and processes. Visualizing the results and plotting analytical graphs prove to be useful under such circumstances. An analytical overview of chaos workflows for an entire month or a year can help in benchmarking release cycles and building a viable cloud-native product. Also a comparative study over time or rather just being able to observe and plot resiliency scores across different types of chaos workflows on different subsystems provide a conclusive summary of the reliability metrics for an application under test (AUT) and the supporting platform or infrastructure.
Prerequisites#
The following should be required before knowing about workflow statistics:
Data flow architecture#
The chaos center automatically detects scheduled chaos workflow runs on all connected agents for a project and provides statistical graphs and visualizations. Data for workflow runs and chaos results from all the agents are stored in a mongoDB database which is then ingested into analytical pipelines in the control plane server to transform the raw data into meaningful insights for browsing and reporting.
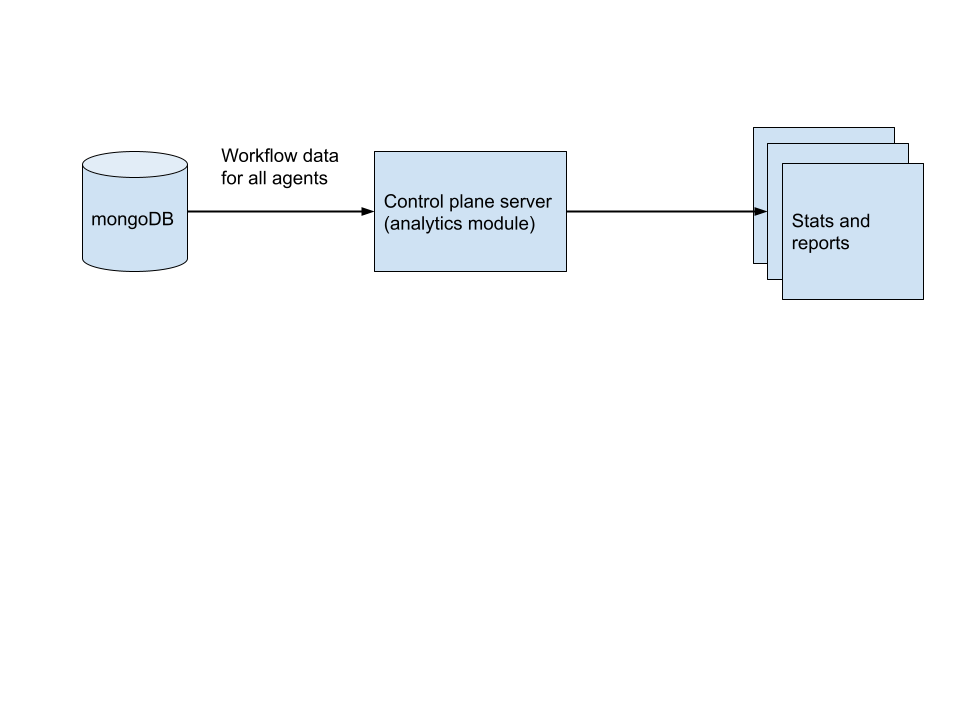 Data flow for statistical analysis
Data flow for statistical analysisChaos engine context#
The context is a user defined label for a chaos engine to indicate the intent or the target of chaos. Some of it's uses are for naming AUT, micro-service, infrastructure resource etc. Engine context can be added or updated by the user via the UI. It is used to filter chaos experiments, results, tests during statistical analysis and for filtering chaos injection events during real time monitoring of application or infrastructure metrics interleaved with chaos. It defaults to the target application label and namespace separated by _ while using chaos center for scheduling chaos workflows.
Chaos workflow subject#
The subject is a user defined label for a chaos workflow to indicate the intent or the target of chaos. Some of it's uses are for naming AUT, micro-service, infrastructure resource etc. Workflow subject can be added or updated by the user via the UI. It is used to filter chaos workflows during statistical analysis and is stored as a metadata for referencing to a particular application group or version on a given target cluster with chaos agent. It defaults to the target application name and namespace separated by _ while using chaos center for scheduling chaos workflows.
Summary#
Statistics of a workflow schedule across its runs and analyzing application performance across workflows on a target cluster's AUT are facilitated via the data stored in the persistent storage (mongoDB), collected by the connected chaos agent plane components like subscriber and chaos-exporter. Engine context and Workflow subject are meant to provide the user with more granular control over the target of chaos while analyzing results or monitoring system or application metrics in real-time under stress or chaos.